Basics of networking
14. Network performance. Methods of reducing network traffic.
14.4. Network performance tests
Network interference
Data loss due to electromagnetic interference can occur in both wireless networks and networks using copper cables. Electrical networks, devices powered by high currents produce electromagnetic radiation.
When any part of a WiFi network is in the vicinity of equipment such as an electric traction train or tram, interference with data transmission can be expected.
Network cables made of copper are similarly affected by electromagnetic radiation. Networks where UTP cables are located too close to electrical cables can be exposed to electromagnetic interference.
If electromagnetic interference is expected in a particular location, use fibre optics as the data carrier; these are resistant to electromagnetic radiation.
Computer network performance tests
The performance of a computer network boils down to determining the throughput, i.e. the amount of information we can send over the tested network in a certain time. The simplest way to determine network performance is therefore to download/send a certain amount of data and measure the time it takes.
The results of a network performance test can be distorted by other factors that are not directly part of the computer network. When sending or downloading data, it is important to remember that it must be read and written to disk. If the computer's hard disk has a maximum read/write speed lower than the network speed, the throughput test result will not show the network performance, but only the read/write result of the data on the hard disk. In this case, we can say that the so-called "bottleneck" of our computer system is the hard disk. Another common factor that skews network performance is the download speed limits applied to file-sharing servers. Because download providers need to ensure that as many clients as possible have access to download files, they cannot allow only one client to reach the maximum download speed when downloading. File servers divide the maximum upload speed from the server to the client by the expected number of clients over a given period of time, so when downloading a file over the internet with a throughput of, say, 300Mbps the maximum transfer is, for example, 10Mbps.
To test the network throughput, we can use any program that downloads/sends data. However, in order to obtain reliable results, it should be repeated many times at different days and times. We can carry out a performance test using programmes such as wget, ping or using dedicated websites for this purpose: speeedtest.net, www.nperf.com.
wget
The wget programme is a console programme most commonly used in the Linux environment. In MS Windows operating systems from version 10 onwards, it is easy to "install" Linux using WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) technology. To carry out a network bandwidth test using the wget programme, issue the following command in the console (text terminal): wget https://ftp.icm.edu.pl/debian/dists/Debian8.11/main/Contents-amd64.gz , this command starts the download from the internet address: https://ftp.icm.edu.pl/debian/dists/Debian8.11/main/Contents-amd64.gz. As we can see in the image below, we get the following information: 26 MB were downloaded at a speed of 11.2 MB/s in 2.3 seconds.
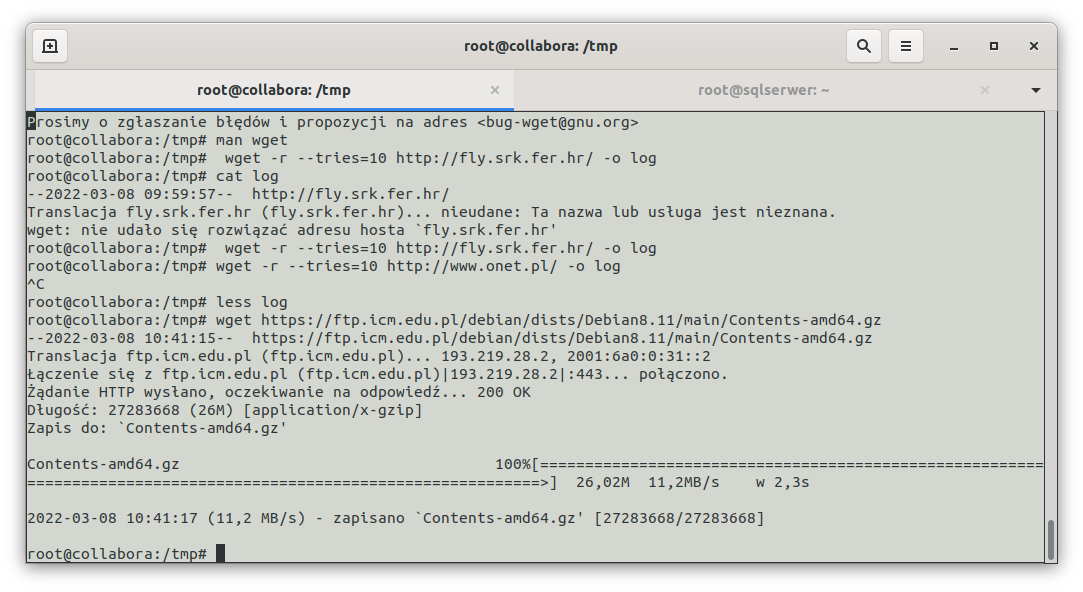
(Figure 1. Network speed test using the wget program)
We can use the wget programme to perform multiple trials simultaneously, example:
wget -r --tries=10 http://www.onet.pl/ -o log
Here we perform a recursive download (-r) of the contents of www.onet.pl , the download attempts are repeated 10 times, the results are recorded in a log file. The results stored in the log file show the time and speed of the transfer given from the web page.
ping
Another console programme available in various operating systems is ping.
Example of network performance test using ping:
ping wp.pl
PING wp.pl (212.77.98.9) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=1 ttl=55 time=16.0 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=2 ttl=55 time=15.3 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=3 ttl=55 time=15.2 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=4 ttl=55 time=15.3 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=5 ttl=55 time=15.2 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=6 ttl=55 time=15.2 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=7 ttl=55 time=15.3 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=8 ttl=55 time=15.3 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=9 ttl=55 time=15.3 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=10 ttl=55 time=15.3 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=11 ttl=55 time=15.2 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=12 ttl=55 time=15.2 ms
64 bytes from www.wp.pl (212.77.98.9): icmp_seq=13 ttl=55 time=15.2 ms
--- wp.pl ping statistics ---
13 packets transmitted, 13 received, 0% packet loss, time 12015ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 15.185/15.307/16.032/0.212 ms
In the example above, an ICMP Echo Request packet was sent to the server with the address www.wp.pl 13 times and the same number of replies were received (ICMP Echo Reply). The last line of the example ( min/avg/max/mdev = 15.185/15.307/16.032/0.212 ms ) contains the result of a test of the speed of transmission of a packet through the network - the smaller the response times, the more efficient our network is.
speedtest.net
There are also web applications for testing upload/download speeds. At https://www.speedtest.net we can perform a test showing both the PING value and the upload and download speeds. The figures below show screenshots of an internet upload test between a network in Kielce (Poland) and a network in Prague (Czech Republic).
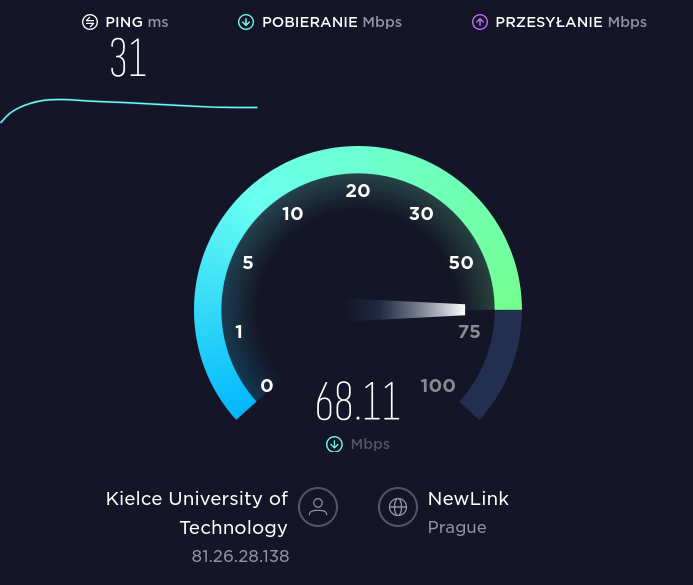
(Figure 2. Network speed test using speedtest.net)
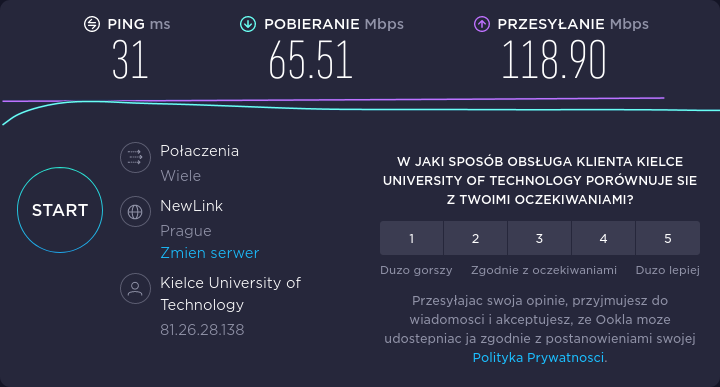
(Figure 3. Result of the network test using speedtest.net)
www.nperf.com
The npref.com web application is similar to speedtes.net. The results are also presented in an attractive graphical form.
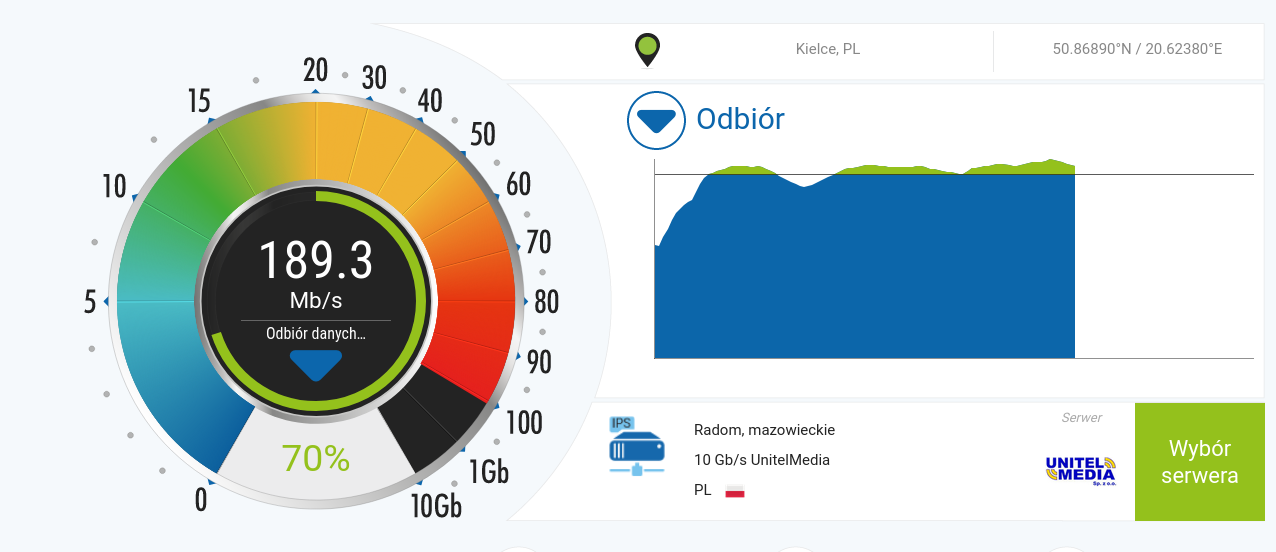
(Figure 4. Network speed test with www.nperf.com)
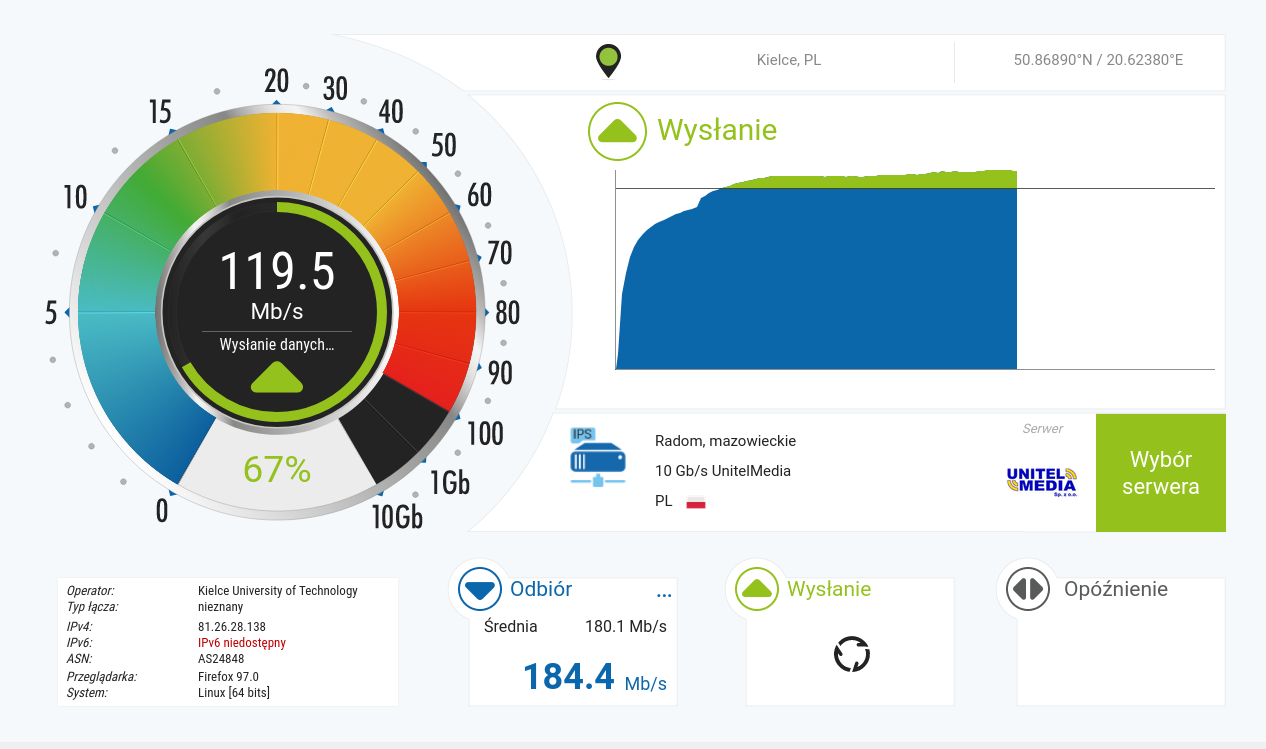
(Figure 5. Network speed test with www.nperf.com)
